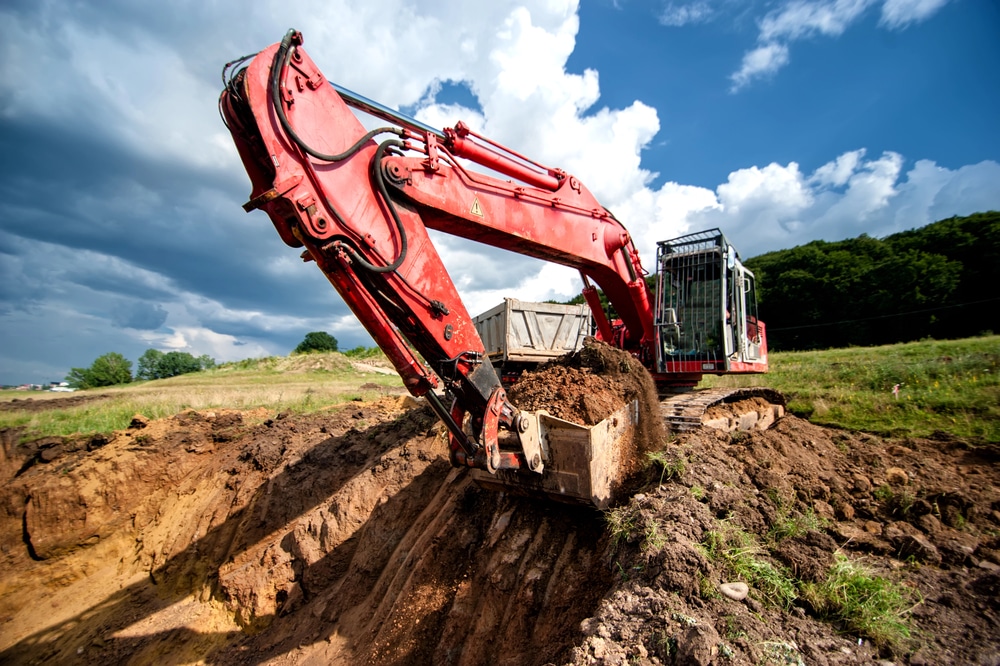
When starting a construction project, a common question arises: What is the difference between excavation and digging? Many people think excavation and digging are the same, but they serve different purposes and involve different methods. Understanding these differences helps property owners save time, money, and effort.
Keep reading to learn more about what is the difference between excavation and digging and how understanding these differences can benefit your next project.
What Is the Difference Between Excavation and Digging?
Understanding what is the difference between excavation and digging can significantly impact your project planning. Here are five key distinctions:
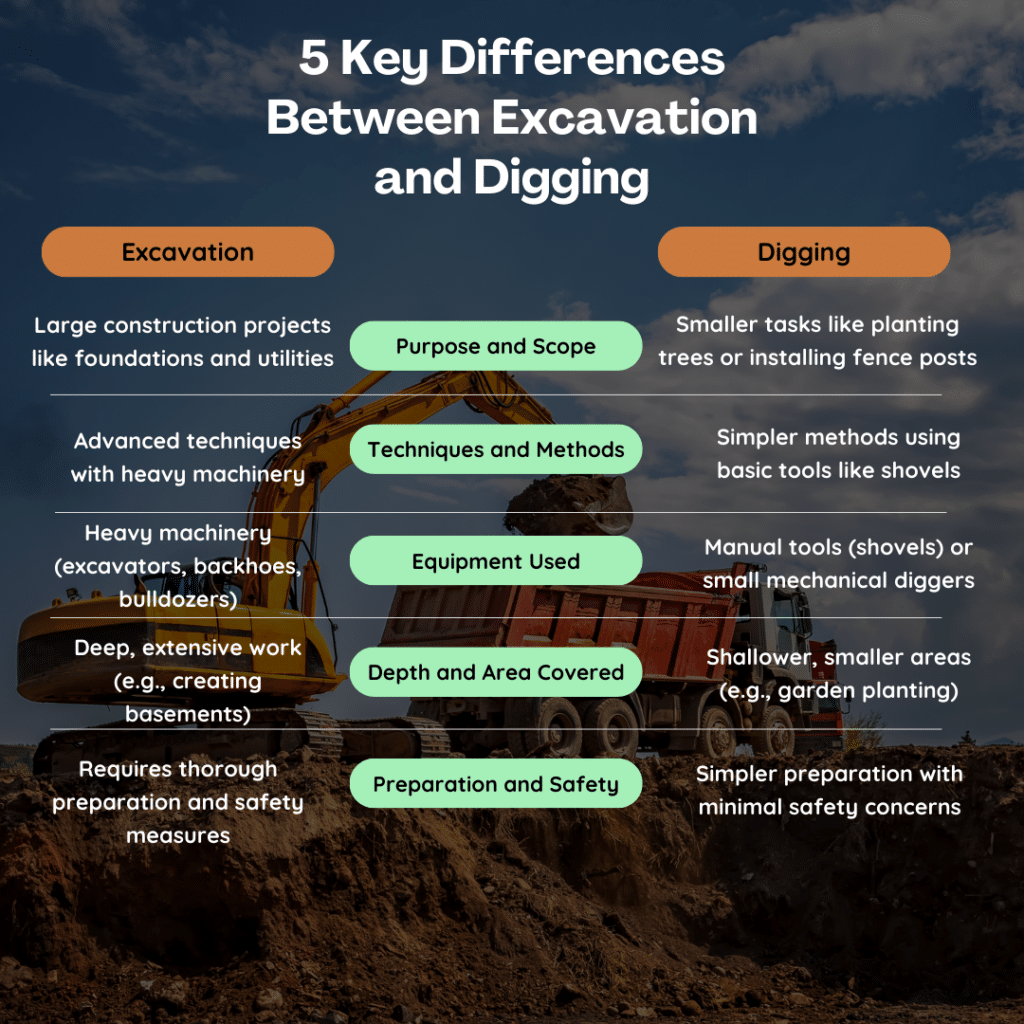
Purpose and Scope
- Excavation is usually part of larger construction projects, such as building foundations, installing underground utilities, or creating large landscape features. It involves detailed planning and precise execution to ensure structural integrity and safety.
- Digging is often for smaller tasks such as planting trees, installing fence posts, or small-scale landscaping. It doesn’t usually require extensive planning or equipment.
Techniques and Methods
- Excavation employs advanced techniques and machinery. Excavators, backhoes, and bulldozers are common tools. The process might involve removing large amounts of earth, rock, or other materials.
- Digging is typically done with simpler tools like shovels or small mechanical diggers. It’s a straightforward process that doesn’t usually require specialized skills.
Equipment Used
- Excavation relies on heavy machinery. Trained professionals operate these machines to handle the complexities and scale of the work. The equipment used is designed for deep, large-scale digging and material removal.
- Digging can often be done manually or with small machinery. It’s more labor-intensive but doesn’t require the heavy-duty equipment that excavation does.
Depth and Area Covered
- Excavation usually involves deeper and more extensive work. For example, creating a basement or a large pond requires removing a significant amount of earth over a wide area.
- Digging is shallower and covers a smaller area. Tasks like garden planting or small trench digging for irrigation systems are typical examples.
Preparation and Safety
- Excavation requires thorough preparation. This includes surveying the land, marking underground utilities, and obtaining necessary permits. Due to the scale of the operation and the equipment involved, safety is a major concern.
- Digging has simpler preparation steps. It might involve marking the area and checking for any small underground obstructions, but it doesn’t usually require the extensive safety measures that excavation does.
Misinterpreting what is the difference between excavation and digging can lead to choosing the wrong method, potentially causing project delays or safety issues.
Is Drilling Considered Excavation?
Drilling is often used in the initial stages of excavation to explore underground conditions. For example, drilling boreholes helps to assess soil composition, rock layers, and water tables before large-scale excavation begins. In this sense, drilling is a preliminary step within the broader excavation process.
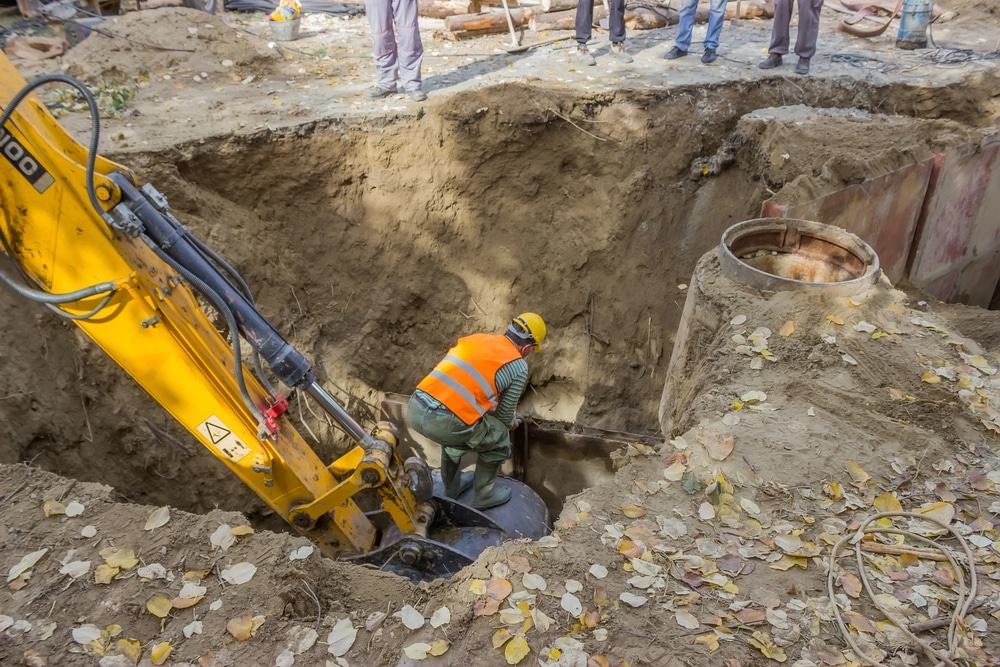

- Techniques and Equipment
Drilling involves specialized equipment like drill rigs and augers. These tools create precise, deep holes in the ground, providing critical information for excavation planning. The drilling process requires skilled operators who understand how to handle the equipment and interpret the data collected.
- Examples
In construction, drilling might install piers or piles that support a building’s foundation. These drilled shafts are essential for stability, especially in unstable soil or high water tables. Another example is drilling for utility lines, where precise holes are needed to run cables or pipes underground.
Drilling as a Separate Activity:
- Purpose
Drilling can also be independent and separate from traditional excavation. This includes drilling for water wells, oil, or natural gas. These projects don’t necessarily involve removing large amounts of earth but instead focus on accessing underground resources.
- Techniques and Equipment
Independent drilling projects use similar equipment to exploratory drilling but are often more specialized. For example, oil drilling rigs are highly complex machines designed to drill to great depths and extract resources.
- Examples
Water well drilling is standard in rural areas with limited access to municipal water systems. Similarly, energy companies conduct oil and gas drilling projects to extract valuable resources beneath the earth’s surface.
Drilling can be considered a part of excavation when it serves as a preliminary step or supports the excavation process. However, it can also stand alone as a distinct activity with specific goals and methods. Understanding what is the difference between excavation and digging helps clarify how drilling fits into these broader categories.
What Does Excavating Land Mean?
Excavation is when you dig up earth, rock, or other stuff from a place to make a hole or hollow. The primary purpose is to prepare the site for construction or other projects. This can include creating building foundations, laying underground utilities, or landscaping.
But what is the difference between excavation and digging? Excavation is more complex and planned than digging. It involves precise measurements and heavy machinery to ensure the site is ready for its intended use.
Steps in Excavation
- Site Survey and Planning
Before any excavation begins, the site must be surveyed to determine its topography, soil composition, and potential hazards. This information is crucial for planning the excavation process.
- Marking and Clearing the Site
The area to be excavated is marked according to the project plans. To clear the site, obstacles, such as trees or existing structures, are removed.
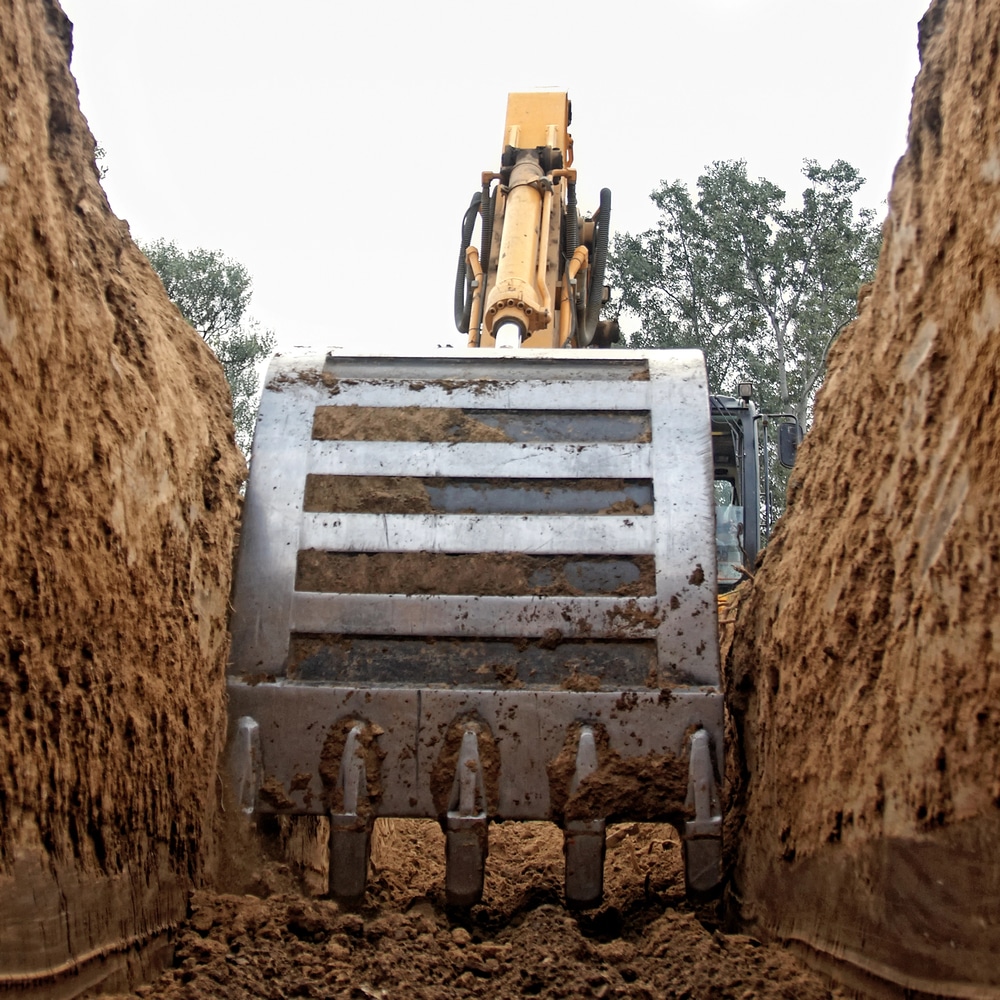

- Digging and Removal
Heavy machinery like excavators and bulldozers dig and remove the earth. The depth and area of excavation depend on the project’s requirements. For instance, creating a building foundation requires precise depth and width specifications.
- Soil and Material Management
The removed earth and materials are relocated within the site for other uses, such as backfilling, or transported off-site for disposal. Proper management of these materials is essential for maintaining site safety and environmental standards.
- Safety Measures:
Safety is a top priority during excavation. This includes securing the site with barriers, ensuring machinery is operated by trained professionals, and monitoring for any signs of instability or hazards.
Understanding what is the difference between excavation and digging helps clarify that excavating land is a detailed, planned process involving more than just removing the earth. Getting the job done right means you need to prepare well, operate the machinery like a pro, and always stick to safety rules.
What Is Considered Excavation?
Understanding what is considered excavation is essential for effective project planning and execution. Here are some points to consider:
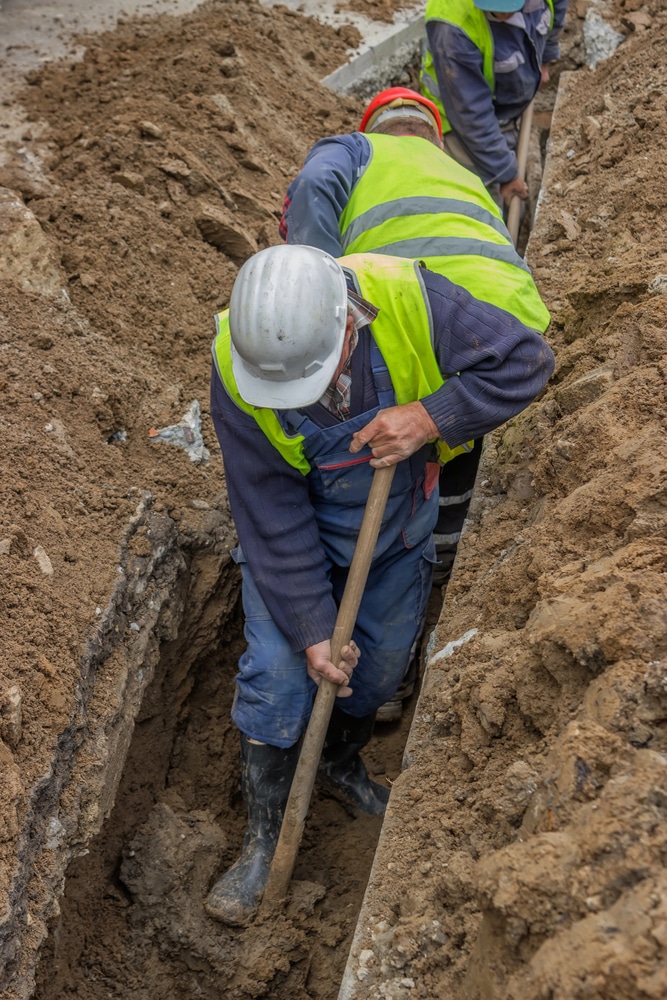

Types of Excavation
- Topsoil excavation involves removing the top layer of soil rich in organic matter to prepare the land for construction or farming. For example, removing topsoil is necessary to prepare a site for building a house.
- Earth excavation involves removing soil beneath the topsoil layer, commonly used for foundations and other structures. An example is digging out soil to lay the foundation for a commercial building.
- Rock excavation involves removing solid rock, often requiring blasting or specialized machinery, and is typically more complex and expensive. For instance, excavating rock is necessary to build tunnels or roads in hilly regions.
- Muck excavation involves removing a mixture of water and soil commonly found in wetlands or waterlogged areas. Clearing muck is essential for constructing drainage systems or roadbeds.
- Trench excavation involves creating narrow, deep trenches for utilities such as water pipes, gas lines, or electrical conduits. Digging trenches is vital for laying underground cables or pipelines.
Purposes of Excavation
- Construction
Excavation is crucial for creating foundations, basements, and underground parking structures, ensuring the stability and safety of these structures.
- Landscaping
Shaping the land for aesthetic and functional purposes, like creating terraces, ponds, or retaining walls, often requires excavation.
- Archaeology
Carefully removing earth to uncover and preserve historic artifacts and sites requires precision to avoid damaging valuable finds.
- Mining
Extracting minerals, metals, and other valuable materials from the earth can involve large-scale operations and significant environmental management.
Safety and Regulations
- Safety Measures
Excavation poses risks such as cave-ins, equipment accidents, and exposure to hazardous materials. Implementing safety measures like shoring, trench boxes, and safety training is essential.
- Regulations
Compliance with local and national laws is crucial, including obtaining permits, conducting environmental assessments, and adhering to safety standards.
Knowing what is the difference between excavation and digging highlights the complexity and scope of excavation activities. Excavation is a detailed, regulated, and safety-focused process that requires careful planning and execution.
Final Thoughts
Knowing what is the difference between excavation and digging is crucial for planning construction or landscaping projects. Excavation involves detailed, regulated processes with advanced machinery while digging is simpler and often manual.
Recognizing these differences ensures projects are executed correctly, avoiding delays and safety issues. Whether preparing a site for a building, installing utilities, or creating landscape features, knowing when to use excavation versus digging is key.
For your excavation, land clearing, and preparation needs, consider Shilling Excavation for efficient and safe project completion.
If you have questions about what is the difference between excavation and digging, please reach out. Being aware of these distinctions can significantly impact your project’s success.





